Thursday, 27 February 2020
Railway Engineering
PART - 01
What is Rails, Definition & Types of Rails
Definition of Rails
A rail is a steel bar extending horizontally between supports which is used as a track for rail road, cars or other vehicles
Types of Rails
Rails can be divided in three types
- Double Headed Rails
- Bull Headed Rails
- Flat Footed Rails
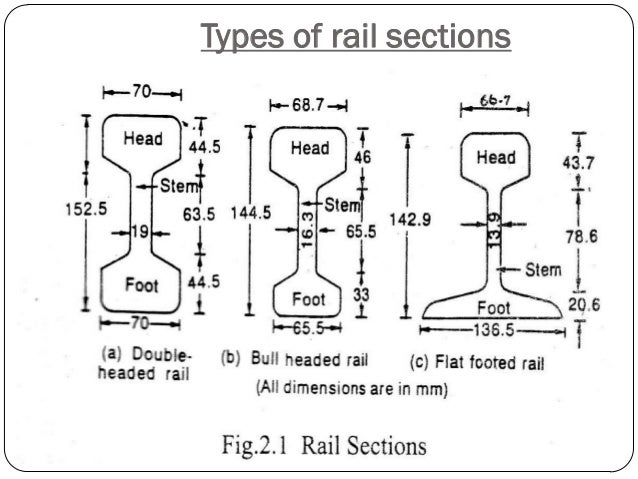
1. Double Headed Rails
These rails indicate the early stage of development. It essentially consists of three parts,
- Upper Table
- Web
- Lower Table
Both the upper and lower tables were identical and they were introduced with the hope of double doubling the life of rails. When the upper table is worn out then the rails can be placed upside down reversed on the chair and so the lower table can be brought into use. But this idea soon turned out to b wrong because due to continuous contract of lower table with the chair made the surface of lower table rough and hence the smooth running of the train was impossible. Therefore, this type of rail is practically out of use. Nowadays, these rails vary in lengths from 20 – 24. A 100 lb double headed rail is shown in the figure.
2. Bull Headed Rails
This type of rail also consists of three parts,
- The Head
- The Web
- The Foot
These rails were made of steel. The head is of larger size than foot and the foot is designed only to hold up properly the wooden keys with which rails are secured. Thus, the foot is designed only to furnish necessary strength and stiffness to rails. Two cast iron chairs are required per each sleeper when these rails are adopted. Their weight ranges from 85lb to 95lb and their length is up to 60 ft.
3. Flat Footed Rails
These rails were first of all invented by Charles Vignoles in 1836 and hence these rails are also called vignols rails. It consist of three parts
The foot is spread out to form a base. This form of rail has become so much popular that about 90% of railway tracks in the world are laid with this form of rails.
Flat footed rails has the following advantages
- They do not need any chair and can be directly spiked or keyed to the sleepers. Thus they are economical.
- They are much stiffer both vertically and laterally. The lateral stiffness is important for curves.
- They are less liable to develop kinks and maintain a more regular top surface than bull headed rails.
- They are cheaper than bull headed rails.
- The loads from wheels of trains are distributed over large number of sleepers and hence larger area which results in greater track stability, longer life of rails and sleepers, reduced maintenance, costs, less rail failure and few interruptions to traffic.
Classification of Railway Sleepers - Advantages and Disadvantages
1. Wooden Sleepers
Wooden sleepers are the ideal type of sleeper. Hence they are universally used. The utility of timber sleepers has not diminished due to the passage of time
Advantages of Wooden Sleepers
- They are cheap and easy to manufacture
- They are easy to handle without damage
- They are more suitable for all types of ballast
- They absorb shocks and vibrations better than other types of sleepers.
- Ideal for track circuited sections
- Fittings are few and simple in design
Disadvantages of Wooden Sleepers
- They are easily liable to attack by vermin and weather
- They are susceptible to fire
- It is difficult to maintain gauge in case of wooden sleepers
- Scrap value is negligible
- Their useful life is short about 12 to 15 years.
2. Steel Sleepers
Due to the increasing shortage of timber in the country and other economic factors have led to the use of steel and concrete sleepers on railways
Advantages of Steel Sleepers
- It is more durable. Its life is about 35 years
- Lesser damage during handling and transport
- It is not susceptible to vermin attack
- It is not susceptible to fire
- Its scrap value is very good
Disadvantages of Steel Sleepers
- It is liable to corrosion.
- Not suitable for track circuiting
- It can be used only for rails for which it is manufactured
- Cracks at rail seats develop during the service.
- Fittings required are greater in number
3. Cast Iron Railway Sleepers
They are further divided into two categories:
- Cast iron pot type sleepers
- Cast iron plate type sleepers
Advantages of Cast Iron Sleepers
- Service life is very long
- Less liable to corrosion
- Form good track for light traffic up to 110 kmph as they form rigid track subjected to vibrations under moving loads without any damping
- Scrap value is high
Disadvantages of Cast Iron Sleepers
- Gauge maintenance is difficult as tie bars get bent up
- Not suitable for circuited track
- Need large number of fittings
- Suitable only for stone ballast
- Heavy traffic and high speeds (>110kmph) will cause loosening of keys and development of high creep
4. Concrete Railway Sleepers
R.C.C and prestressed concrete sleepers are now replacing other types of sleepers except in some special circumstances like bridges etc. where wooden sleepers are used. Concrete sleepers may be of two types:
- Mono Block Concrete Sleepers
- TWIN BLOCK Concrete sleepers
Advantages of Concrete Sleepers
- It is more durable having greater life (up to 50years)
- It is economical as compare to wood and steel.
- Easy to manufacture.
- It is not susceptible to vermin attack
- It is not susceptible to fire
- Good for track circuited areas
Disadvantages of Concrete Sleepers
- It is brittle and cracks without warning.
- It cannot be repaired, and required replacement.
- Fittings required are greater in number.
- No scrap value
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)