- Viscosity
It is defined as the property of a liquid which offers resistance to the movement of one layer of liquid over another adjacent layer of liquid.
The viscosity of a liquid is due to cohesion and interaction between particle.
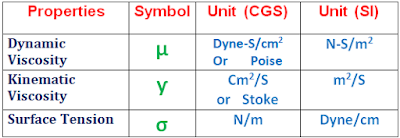
Viscosity is also known as Absolute Viscosity or Dynamic Viscosity.
- Kinematic Viscosity
It is defined as the ratio of dynamic viscosity to the density of liquid.
- Compressibility
It is that property of liquid by virtue of which liquids undergo a change in volume with the change in pressure.
The compressibility is the reciprocal of bulk modulus of elasticity, which is defined as the ratio of compressive stress to volumetric strain.
- Surface Tension
The tensile force acting on the surface of a liquid in contact with a gas or another immiscible liquid.
The contact surface behave like a membrane.
- Capillarity
It is defined as a phenomenon of rise or fall of a liquid surface in a small vertical tube held in a liquid relative to the general level of the liquid.
- Symbols & Units
Thank You